Last Updated on August 1, 2019 by Karl Thompson
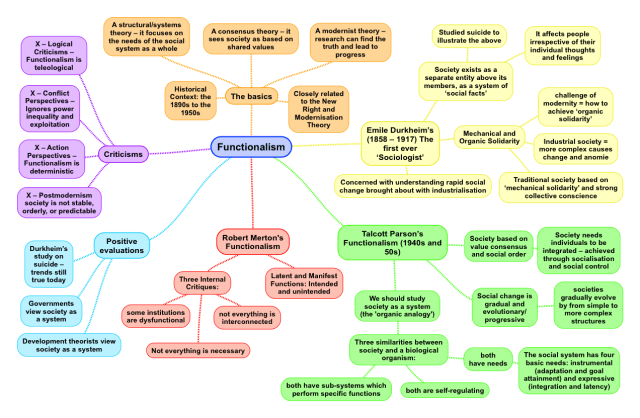
Functionalism as a Structural/Systems Theory – it focuses on the needs of the social system as a whole; it is a consensus theory – it sees society as based on shared values; it is also a modernist theory – it believes that research can find the truth and lead to progress. Functionalism is closely related to the New Right and Modernisation Theory.
Introduction/ Society as a System
- Historical Context: the 1890s to the 1950s
- Parsons uses the term ‘organic analogy’ to describe society.
- Parsons sees three similarities between society and a biological organism: both are self-regulating, both have needs, both have sub-systems which perform specific functions.
Emile Durkheim’s Functionalism (1858 – 1917) – The first ever ‘Sociologist’
- Concerned with understanding rapid social change brought about with industrialisation
- Traditional society based on ‘mechanical solidarity’ and strong collective conscience
- Industrial society = more complex causes change and anomie, challenge of modernity = how to achieve ‘organic solidarity’
- Society exists as a separate entity above its members, as a system of ‘social facts’. It affects people irrespective of their individual thoughts and feelings.
- Studied suicide to illustrate the above.
Talcott Parson’s Functionalism
- Society is based on value consensus and social order
- Society needs individuals to be integrated – this is achieved through socialisation and social control
- The social system has four basic needs: instrumental (adaptation and goal attainment) and expressive (integration and latency)
- Social change is gradual and evolutionary/ progressive – societies gradually evolve by moving from simple to more complex and larger structures.
Robert Merton’s Functionalism
- Merton’s Three Internal Critiques of Functionalism: Not everything is necessary; not everything is interconnected; some institutions are dysfunctional
- Merton’s ideas of Latent and Manifest Functions: Intended and unintended (so functions may be more complex than Parson’s suggests)
Overall Evaluations of Functionalism
- Durkheim’s study on suicide – trends still true today
- Governments view society as a system
- Development theorists view society as a system.
- X – Logical Criticisms – Functionalism is teleological – it explains an institutions existence in terms of its effect, and the effect may not be necessary
- X – Conflict Perspectives – Functionalism ignores power inequality and exploitatio
- X – Action Perspectives – Functionalism is deterministic
- X – Postmodernist Critiques – society is not as stable, orderly, or predictable as Functionalists suggest.
Functionalism applied to other topic areas within sociology
The Functionalist perspective on the family
- The four universal functions of the family
- Functional fit theory
- Primary socialisation
- Stabilisation of adult personalities
- Traditional gender role
The Functionalist perspective on education
- Secondary socialisation
- Social Solidarity
- Skills for working
- Meritocracy
- Role Allocation
Modernisation Theory (Functionalism applied to development)
- Aid injections and five stages of growth
- Cultural Barriers
- Capitalist/ Industrial model of development
Functionalist and Social Control theories of crime
- Bonds of attachment theory
- Positive Functions of Crime
- Inevitability of crime
Functionalist research methods – Positivism
- Social Facts
- Objectivity
- Official Statistics
- Correlations
- Generaliseablity
- Science
If you like this sort of revision-thang, then why not contribute to my early retirement fund and buy these revision notes for Theory and Methods – they’re structured as in the picture below, and cost less than a pint of yer finest ale!
The notes cover the following sub-topics:
- Functionalism
- Marxism
- Feminism
- Social Action Theory
- Postmodernism
- Late Modernism
- Sociology and Social Policy
Related Posts
The Functionalist Perspective on Society – Summary Grid covering the Functionalist perspective on the family, education, crime and global development (modernisation theory)
The Functionalist Perspective on Society – Class Notes
Marxist Theory for second year sociology – Knowledge Check List



One thought on “The Functionalist Theory of Society for A Level Sociology – Revision Notes”